在css3中,可以使用transform属性配合rotateY()、rotateX()等3d旋转函数来实现3d翻转效果。rotateX()可以使元素绕其X轴旋转给定角度,rotateY()可以使元素绕其Y轴旋转给定角度。

本教程操作环境:windows7系统、CSS3&&HTML5版、Dell G3电脑。
一、实现一张图片的翻转
1、HTML结构
<div class="stage"> <div class="flipBox"> <figure class="pic front">Front</figure> <figure class="pic back">Back</figure> </div> </div>
上述HTML的结构是:
- p.stage规定了一个3D舞台,基本上所有使用CSS3 3D变换的实现都会这么做,规定perspective样式从而达到透视效果
- p.flipBox是真正实现翻面的容器,稍后将对它进行3D变换
- figure代表两张图片,一张是正面,一张是背面
思路是:将figure.front和figure.back作为翻转图片的正反面。图片翻转后,figure.back将变成面对用户的那一面,figure.front将背对用户。
初始状态下figure.back是水平翻转过的(即transform: rotateY(180deg)),这样图片翻转后背面的文字将正着显示(否则翻转过来以后背面的文字是倒着的——因为反转之前是正着的嘛~)。
3、CSS结构
body,figure { margin: 0; padding: 0; } .stage { width: 200px; height: 100px; margin: 40px; perspective: 1000px; } .flipBox { width: 200px; height: 100px; position: relative; transform-style: preserve-3d; transition: transform 1s; } .pic { width: 200px; height: 100px; font-size: 24px; color: #fff; line-height: 100px; text-align: center; position: absolute; top: 0; left: 0; backface-visibility: hidden; } .front { background: #f00; } .back { background: #090; transform: rotateY(180deg); }
现在分析每个元素的CSS:
body,figure { margin: 0; padding: 0; }
没什么好说的,去掉内外边距!
.stage { width: 200px; height: 100px; margin: 40px; perspective: 1000px; }
为3D舞台定义样式。margin是为了距离浏览器左边和上边有一些距离,让变换显示的更完整。perspective规定了3D元素距摄像机(或人眼)的距离,值越小3D元素离人眼越近,值越大3D元素离人眼越远。
.flipBox { width: 200px; height: 100px; position: relative; transform-style: preserve-3d; transition: transform 1s; }
为翻转盒子定义样式。这个元素是真正进行3D变换的元素。其position属性是为其两个子figure元素创造定位点,以便两个子figure元素定位到p.flipBox的左上角实现两张图片的对齐。transform-style属性是必须的,这规定了p.flipBox元素的后代元素是以哪种形式进行3D变换(preserve-3d表示后代元素任然以3d的模式进行变换;另一个值flat表示只对p.flipBox进行3D变换,后代元素则只是p.flipBox平面中的内容,不进行3D变换),这和After Effect中的伪3D十分相似。transition规定只变换transform属性,时间为1s.
.pic { width: 200px; height: 100px; font-size: 24px; color: #fff; line-height: 100px; text-align: center; position: absolute; top: 0; left: 0; backface-visibility: hidden; }
为两张图片(这里的两个figure)规定统一的样式。使用绝对定位,定位到p.flipBox的左上角,而两个figure的大小又是一样的,所以完美重叠。backface-visibility是一个重要的属性,它规定背对用户的3D元素是否显示,这里应该规定为不显示(hidden),否则不该显示背面的时候背面会显示出来。比如初始状态,显然不应该显示figure.back,但又因为figure.back是后渲染的,所以会覆盖在figure.front上,我们之前为figure.back规定了transform: rotateY(180deg),所以figure.front是背对用户的,将不显示。再比如翻转过后,figure.front会挡在figure.back前面,不过此时figure.front将会背对用户,所以被backface-visibility隐藏了,这正是我们想要的。
.front { background: #f00; }
规定了图片正面为红色。
.back { background: #090; transform: rotateY(180deg); }
规定了图片背面为绿色,同时,transform: rotateY(180deg)规定在初始状态,figure.back是水平翻转180°的。
3、开始旋转图片
.stage:hover .flipBox { transform: rotateY(-180deg); }
当鼠标移入3D舞台时,将p.flipBox旋转-180°,实现图片翻转效果。这里让p.flipBox旋转+180°也是可以的,只是旋转的方向不同罢了。 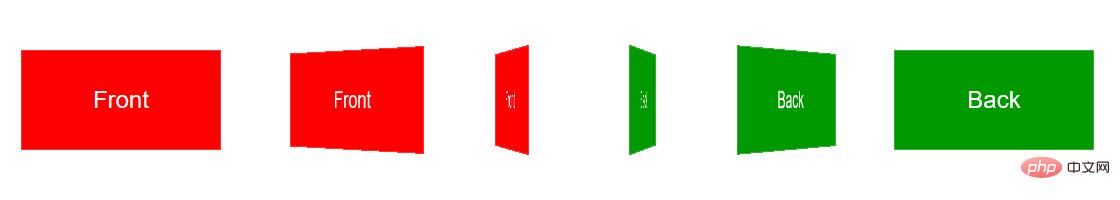
二、案例
1、图片准备
为减少HTTP请求,这里使用精灵图。 
图片大小为200*200,分上下两部分,上方为翻转图片的正面(黑白),下方为翻转图片的背面(彩色)。上方和下方的logo都经过水平居中和垂直居中,以保证翻转前后logo位置一致。
2、代码实现
<!doctype html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>JavaScript Study</title> <style> html,body,ul,li,a,figure,h4 { padding: 0; margin: 0; } ul { list-style: none; } h4 { display: none; } .Stage { width: 604px; height: 203px; margin: 50px; border-left: 1px solid #f5f5f5; border-top: 1px solid #f5f5f5; perspective: 10000px; } .trigger { display: block; float: left; width: 200px; height:100px; border-right: 1px solid #f5f5f5; border-bottom: 1px solid #f5f5f5; position: relative; } .flipBox { display: block; width: 100%; height: 100%; transform-style: preserve-3d; transition: transform 1.2s; transition-delay: 0.03s; } .trigger:hover .flipBox { transform: perspective(10000px) rotateY(-180deg); /*这里的perspective为每个flipBox规定单独的视点距离,解决Chrome中统一视点的问题*/ } .plane { width: 200px; height: 100px; position: absolute; top: 0; left: 0; backface-visibility: hidden; } .back { transform: rotateY(180deg); } .logo1 figure.front { background: url("pic.png") center 0 no-repeat; } .logo2 figure.front { background: url("pic_2.png") center 0 no-repeat; } .logo3 figure.front { background: url("pic_3.png") center 0 no-repeat; } .logo4 figure.front { background: url("pic_4.png") center 0 no-repeat; } .logo5 figure.front { background: url("pic_5.png") center 0 no-repeat; } .logo6 figure.front { background: url("pic_6.png") center 0 no-repeat; } .logo1 figure.back { background: url("pic.png") center -100px no-repeat; } .logo2 figure.back { background: url("pic_2.png") center -100px no-repeat; } .logo3 figure.back { background: url("pic_3.png") center -100px no-repeat; } .logo4 figure.back { background: url("pic_4.png") center -100px no-repeat; } .logo5 figure.back { background: url("pic_5.png") center -100px no-repeat; } .logo6 figure.back { background: url("pic_6.png") center -100px no-repeat; } </style> </head> <body> <div> <ul> <li> <a class="flipBox logo1" href="#"> <h4>Fun Games</h4> <figure class="plane front"></figure> <figure class="plane back"></figure> </a> </li> <li> <a class="flipBox logo2" href="#"> <h4>Man Style</h4> <figure class="plane front"></figure> <figure class="plane back"></figure> </a> </li> <li> <a class="flipBox logo3" href="#"> <h4>Sims.</h4> <figure class="plane front"></figure> <figure class="plane back"></figure> </a> </li> <li> <a class="flipBox logo4" href="#"> <h4>Googla</h4> <figure class="plane front"></figure> <figure class="plane back"></figure> </a> </li> <li> <a class="flipBox logo5" href="#"> <h4>JavaScript</h4> <figure class="plane front"></figure> <figure class="plane back"></figure> </a> </li> <li> <a class="flipBox logo6" href="#"> <h4>Felix</h4> <figure class="plane front"></figure> <figure class="plane back"></figure> </a> </li> </ul> </div> </body> </html>


(学习视频分享:css视频教程)
 站长资讯网
站长资讯网