下面由Laravel教程栏目带大家推荐介绍关于Laravel Carbon 扩展包,希望对大家有所帮助!
-
Introduction
Carbon *继承了PHP的 *Datetime *类和JsonSerialiable。所以 *Carbon *中没有涉及到的,但在 *Datetime *和JsonSerializable*中已经实现的方法都是可以使用的。
class Carbon extends DateTime implements JsonSerializable { //code here}
Carbon 类声明在 Carbon 命名空间下,可以通过引入命名空间的方式来代替每次输入完整的类名。
<?php use CarbonCarbon;
要特别留意是否使用了正确的时区,比如的所有差异比较都使用或者系统设定的时区
$dtToronto = Carbon::create(2012, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 'America/Toronto'); $dtVancouver = Carbon::create(2012, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 'America/Vancouver'); echo $dtVancouver->diffInHours($dtToronto); //
以上进行的时间比较是在提供的 Carbon 实例所在的时区下完成的。例如作者所在的时区为 东京时间减13 小时,因此在下午一点后。Carbon::now(‘Asia/Tokyo’)->isToday() 将会返回 false ,如果在调用 now() 时设置时区为东京时区,接下来的操作都使用东京时区是说不过去的。所以在与 *now() *创建的实例进行比较时,默认是在当前时区下完成的。
-
Instantiation
有几种不同的方法可以创建一个新的Carbon实例。首先是构造函数。它覆盖父构造函数,您最好阅读PHP手册中的第一个参数,并了解它所接受的日期/时间字符串格式。您可能会发现自己很少使用构造函数,而是依赖于显式静态方法来提高可读性
$carbon = new Carbon(); // 等同于 Carbon::now() $carbon = new Carbon('first day of January 2008', 'America/Vancouver'); echo get_class($carbon); // 'CarbonCarbon' $carbon = Carbon::now(-5);//1表示英国伦敦,2表示法国巴黎
您将在上面注意到,timezone(2nd)参数是作为字符串和整数而不是DateTimeZone实例传递的。所有DateTimeZone参数都已被增强,因此您可以将一个DateTimeZone实例、字符串或整型偏移量传递给GMT,并为您创建时区。在下一个示例中再次显示了这一点,该示例还介绍了now()函数。
$nowInLondonTz = Carbon::now(new DateTimeZone('Europe/London')); // 或者以字符串形式只传时区 $nowInLondonTz = Carbon::now('Europe/London');// 或者在DST期间创建一个时区为+1到GMT的日期,然后传递一个整数echo Carbon::now(1)->tzName; // Europe/London
如果您真的喜欢您的动态方法调用,并且对使用构造函数时所需的额外的行或难看的括号感到失望,那么您将喜欢parse方法。
echo (new Carbon('first day of December 2008'))->addWeeks(2); // 2008-12-15 00:00:00 echo Carbon::parse('first day of December 2008')->addWeeks(2); // 2008-12-15 00:00:00
NOTE*:在PHP 5.4* 之前(new MyClass())->method()会报语法错误**, 如果你使用**PHP 5.3, 你需要创建一个变量然后再调用方法:
$date = new Carbon('first day of December 2008'); echo $date->addWeeks(2);
传递给Carbon:::parse或new Carbon的字符串可以表示相对时间(next sunday, tomorrow, first day of next month, last year)或绝对时间(first day of December 2008, 2017-01-06)。您可以用Carbon::hasRelativeKeywords()测试一个字符串是否会产生一个相对或绝对日期。
$string = 'first day of next month'; if (strtotime($string) === false) { echo "'$string' is not a valid date/time string."; } elseif (Carbon::hasRelativeKeywords($string)) { echo "'$string' is a relative valid date/time string, it will returns different dates depending on the current date."; } else { echo "'$string' is an absolute date/time string, it will always returns the same date."; }
为了配合now(),还存在一些静态的实例化助手来创建广为人知的实例。这里唯一需要注意的是,today()、tomorrow()和yesterday()除了按照预期的行为,都接受一个时区参数,每个参数的时间值都设置为00:00:00。
$now = Carbon::now(); echo $now; // 2018-07-26 16:25:49 $today = Carbon::today(); echo $today; // 2018-07-26 00:00:00 $tomorrow = Carbon::tomorrow('Europe/London'); echo $tomorrow; // 2018-07-27 00:00:00 $yesterday = Carbon::yesterday(); echo $yesterday; // 2018-07-25 00:00:00
下一组静态助手是createXXX() 函数。大多数静态create函数允许您提供许多个或少量的参数,并为所有其他参数提供默认值。通常默认值是当前日期、时间或时区。更高的值将适当地包装,但无效的值将抛出一个InvalidArgumentException,并附带一条信息。错误消息从DateTime:::getLastErrors()调用中获取。
Carbon::createFromDate($year, $month, $day, $tz); Carbon::createFromTime($hour, $minute, $second, $tz); Carbon::createFromTimeString("$hour:$minute:$second", $tz); Carbon::create($year, $month, $day, $hour, $minute, $second, $tz);
createFromDate() 的默认值是当前时间. createFromTime() 默认值是今天. create()如果不传参数也是当前时间. 与前面一样,$tz默认设置为当前时区,否则可以是DateTimeZone实例,也可以是字符串时区值。默认值(模拟底层PHP库)的唯一特殊情况发生在指定了小时值但没有分钟或秒时,它们将默认为0。
注:***createFromTime()** will default the date to today**。小编经实战代码打印出来发现**createFromTime()**的默认值也是当前时间,不是今天(时分秒并不是**00:00:00**)。***
$xmasThisYear = Carbon::createFromDate(null, 12, 25); // Year默认值是今年 $Y2K = Carbon::create(2000, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0); // 等价于Carbon::createMidnightDate(2000, 1, 1) $alsoY2K = Carbon::create(1999, 12, 31, 24); $noonLondonTz = Carbon::createFromTime(12, 0, 0, 'Europe/London'); $teaTime = Carbon::createFromTimeString('17:00:00', 'Europe/London'); // A two digit minute could not be found try { Carbon::create(1975, 5, 21, 22, -2, 0); } catch(InvalidArgumentException $x) { echo $x->getMessage()}
创建异常发生在使用负值上,而不是在溢出上,要获取溢出上的异常,请使用createSafe()
echo Carbon::create(2000, 1, 35, 13, 0, 0);// 2000-02-04 13:00:00 //(1月有31天,4天自动加上去转换成了2月4号) try { Carbon::createSafe(2000, 1, 35, 13, 0, 0); } catch (CarbonExceptionsInvalidDateException $exp) { echo $exp->getMessage(); }// 会报错:day : 35 is not a valid value.
NOTE1:2018-02-29会产生一个异常,而2020-02-29不会产生异常,因为2020年是闰年。
NOTE2:Carbon::createSafe(2014,3,30,1,30,0,’Europe/London’);从PHP 5.4开始也会产生一个异常,因为在夏令时跳过一个小时,但是在PHP 5.4之前,它只会创建这个无效的日期。
Carbon::createFromFormat($format, $time, $tz);
createFromFormat()是最基本的php函数DateTime:::createFromFormat的包装器。不同的是,$tz参数可以是DateTimeZone实例或字符串时区值。此外,如果格式有错误,这个函数将调用DateTime::getLastErrors()方法,然后抛出一个InvalidArgumentException,错误作为消息。如果您查看上面的createXX()函数的源代码,它们都会调用createFromFormat()。
echo Carbon::createFromFormat('Y-m-d H', '1975-05-21 22')->toDateTimeString(); // 1975-05-21 22:00:00
最后三个create函数用于使用unix时间戳。第一个将创建一个与给定的时间戳相等的Carbon实例,并将设置时区或默认为当前时区。第二个createFromTimestampUTC()是不同的,因为时区将保持UTC(GMT)。第二种方法与Carbon: createFromFormat(‘@’.$timestamp)的作用相同,但我只是让它更明确了一点。第三个是createFromTimestampMs(),它接受以毫秒而不是秒为单位的时间戳。也允许使用负时间戳。
echo Carbon::createFromTimestamp(-1)->toDateTimeString(); // 1969-12-31 18:59:59 echo Carbon::createFromTimestamp(-1, 'Europe/London')->toDateTimeString(); // 1970-01-01 00:59:59 echo Carbon::createFromTimestampUTC(-1)->toDateTimeString(); // 1969-12-31 23:59:59echo Carbon::createFromTimestampMs(1)->format('Y-m-dTH:i:s.uP T'); // 1969-12-31T19:00:00.001000-05:00 EST echo Carbon::createFromTimestampMs(1, 'Europe/London')->format('Y-m-dTH:i:s.uP T'); // 1970-01-01T01:00:00.001000+01:00 BST
您还可以copy()在现有Carbon实例上创建。如预期的那样,日期、时间和时区值都被复制到新实例。
$dt = Carbon::now(); echo $dt->diffInYears($dt->copy()->addYear()); // 1
// $dt 实例没有改变,任然是Carbon:now()
您可以在现有的Carbon实例上使用nowWithSameTz()来在相同的时区中获取一个新的实例。
$meeting = Carbon::createFromTime(19, 15, 00, 'Africa/Johannesburg');// 19:15 in Johannesburg echo 'Meeting starts at '.$meeting->format('H:i').' in Johannesburg.'; // Meeting starts at 19:15 in Johannesburg.// now in Johannesburg echo "It's ".$meeting->nowWithSameTz()->format('H:i').' right now in Johannesburg.'; // It's 09:37 right now in Johannesburg.
最后,如果您发现自己从另一个库继承了DateTime实例,不要害怕!您可以通过友好的instance()方法创建一个Carbon实例。或者使用更灵活的方法make(),它可以从DateTime、Carbon或string返回一个新的Carbon实例,否则它只返回null。
$dt = new DateTime('first day of January 2008'); // <== instance from another API $carbon = Carbon::instance($dt); echo get_class($carbon); // 'CarbonCarbon' echo $carbon->toDateTimeString(); // 2008-01-01 00:00:00
关于微秒的简要说明。PHP DateTime对象允许您设置一个微秒值,但是忽略它的所有日期数学。现在,1.12.0的Carbon在实例化或复制操作过程中支持微秒,并在默认情况下使用format()方法。
$dt = Carbon::parse('1975-05-21 22:23:00.123456'); echo $dt->micro; // echo $dt->copy()->micro; //
在PHP 7.1之前 DateTime微秒未添加到“now”实例,并且之后不能更改,这意味着:
$date = new DateTime('now'); echo $date->format('u'); // display current microtime in PHP >= 7.1 (expect a bug in PHP 7.1.3 only)// display 000000 before PHP 7.1 $date = new DateTime('2001-01-01T00:00:00.123456Z'); echo $date->format('u'); // display 123456 in all PHP versions$date->modify('00:00:00.987654');echo $date->format('u');// display 987654 in PHP >= 7.1// display 123456 before PHP 7.1
为了解决这个限制,我们在PHP < 7.1中调用了microseconds,但是这个特性在需要时可以被禁用(PHP >= 7.1):
Carbon::useMicrosecondsFallback(false);var_dump(Carbon::isMicrosecondsFallbackEnabled()); // false echo Carbon::now()->micro; // 0 in PHP < 7.1, microtime in PHP >= 7.1Carbon::useMicrosecondsFallback(true); // default value var_dump(Carbon::isMicrosecondsFallbackEnabled()); // trueecho Carbon::now()->micro; // microtime in all PHP version
是否需要遍历一些日期以找到最早或最近的日期?不知道如何设置初始最大值/最小值?现在有两个助手可以帮助你做出简单的决定:
echo Carbon::maxValue(); // '9999-12-31 23:59:59'echo Carbon::minValue(); // '0001-01-01 00:00:00'
最小和最大值主要取决于系统(32位或64位)。
使用32位OS系统或32位版本的PHP(您可以在PHP中使用PHP_INT_SIZE == 4来检查它),最小值是0-unix-timestamp(1970-01-01 00:00:00),最大值是常量PHP_INT_MAX给出的时间戳。
使用64位OS系统和64位PHP版本,最小值为01-01 00:00,最大值为9999-12-31 23:59:59。
-
Localization
不幸的是,基类DateTime没有任何本地化支持。为了开始本地化支持,还添加了一个formatLocalized($format)方法。实现使用当前实例时间戳对strftime进行调用。如果您首先使用PHP函数setlocale()设置当前的语言环境,那么返回的字符串将被格式化为正确的语言环境。
$newLocale = setlocale(LC_TIME, 'German'); if ($newLocale === false) { echo '"German" locale is not installed on your machine, it may have a different name a different name on your machine or you may need to install it.'; }echo $dt->formatLocalized('%A %d %B %Y'); // Mittwoch 21 Mai 1975 setlocale(LC_TIME, 'English'); echo $dt->formatLocalized('%A %d %B %Y'); // Wednesday 21 May 1975 setlocale(LC_TIME, ''); // reset locale
diffForHumans()也被定位。您可以通过使用静态Carbon::setLocale()函数来设置Carbon locale(),并使用Carbon::getLocale()获取当前的设置。
Carbon::setLocale('de'); echo Carbon::getLocale(); // de echo Carbon::now()->addYear()->diffForHumans(); // in 1 Jahr Carbon::setLocale('en'); echo Carbon::getLocale(); // en
或者,您可以将一些代码与给定的语言环境隔离:
Carbon::executeWithLocale('de', function ($newLocale) { // You can optionally get $newLocale as the first argument of the closure // It will be set to the new locale or false if the locale was not found. echo Carbon::now()->addYear()->diffForHumans(); }); // in 1 Jahr // outside the function the locale did not change echo Carbon::getLocale(); // en // or same using a return statement$french = Carbon::executeWithLocale('fr', function () {return Carbon::now()->addYear()->diffForHumans();}); echo $french; // dans 1 an
有些语言需要打印utf8编码(主要以. utf8结尾的语言环境包)。在本例中,您可以使用静态方法"php
Carbon::setUtf8()对对utf8字符集的formatlocalized()调用的结果进行编码。 setlocale(LC_TIME, 'Spanish'); $dt = Carbon::create(2016, 01, 06, 00, 00, 00); Carbon::setUtf8(false); echo $dt->formatLocalized('%A %d %B %Y'); // mi�rcoles 06 enero 2016 Carbon::setUtf8(true); echo $dt->formatLocalized('%A %d %B %Y'); // miércoles 06 enero 2016 Carbon::setUtf8(false); setlocale(LC_TIME, '');
在Linux上
如果您在翻译方面有问题,请检查系统中安装的地区(本地和生产)。
区域设置-列出已启用的区域设置。
sudo locale-gen fr_FR。UTF-8安装一个新的语言环境。
sudo dpkg-reconfigure locale来发布所有启用的locale。
并重启系统。
您可以通过以下方式自定义现有语言:
Carbon::setLocale('en'); $translator = Carbon::getTranslator(); $translator->setMessages('en', array( 'day' => ':count boring day|:count boring days', )); $date1 = Carbon::create(2018, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0); $date2 = Carbon::create(2018, 1, 4, 4, 0, 0); echo $date1->diffForHumans($date2, true, false, 2); // 3 boring days 4 hours$translator->resetMessages('en'); // reset language customizations for en language
请注意,您还可以使用另一个转换器Carbon::setTranslator($custom),只要给定的转换器继承了SymfonyComponentTranslationTranslatorInterface。 因此,对格式本地化、getter(如localeMonth、localedayayofweek和短变体)的语言环境支持是由安装在操作系统中的语言环境驱动的。对于其他翻译,由于碳社区的支持,它在内部得到了支持。您可以使用以下方法检查支持的内容:
echo implode(', ', array_slice(Carbon::getAvailableLocales(), 0, 3)).'...'; // af, ar, ar_Shakl... // Support diff syntax (before, after, from now, ago) var_dump(Carbon::localeHasDiffSyntax('en')); // bool(true) var_dump(Carbon::localeHasDiffSyntax('zh_TW')); // bool(true) // Support 1-day diff words (just now, yesterday, tomorrow) var_dump(Carbon::localeHasDiffOneDayWords('en')); // bool(true) var_dump(Carbon::localeHasDiffOneDayWords('zh_TW')); // bool(false) // Support 2-days diff words (before yesterday, after tomorrow)var_dump(Carbon::localeHasDiffTwoDayWords('en')); // bool(true) var_dump(Carbon::localeHasDiffTwoDayWords('zh_TW')); // bool(false) // Support short units (1y = 1 year, 1mo = 1 month, etc.) var_dump(Carbon::localeHasShortUnits('en')); // bool(true)var_dump(Carbon::localeHasShortUnits('zh_TW')); // bool(false)// Support period syntax (X times, every X, from X, to X)var_dump(Carbon::localeHasPeriodSyntax('en')); // bool(true)var_dump(Carbon::localeHasPeriodSyntax('zh_TW')); // bool(false)
以下是最后一个碳版本支持的73个地区的概述:
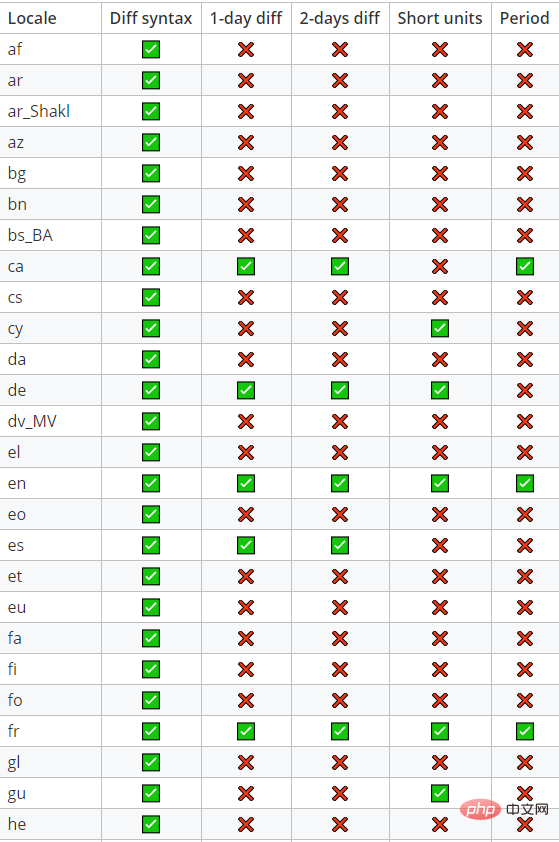
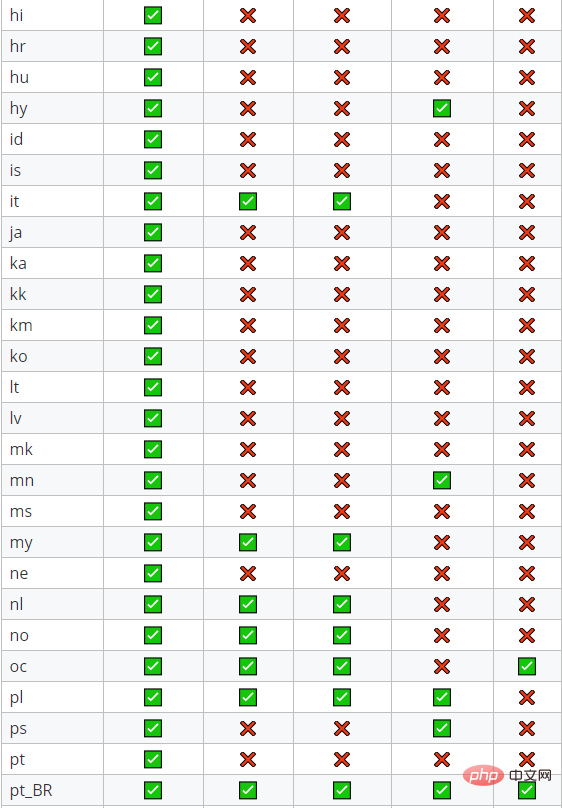
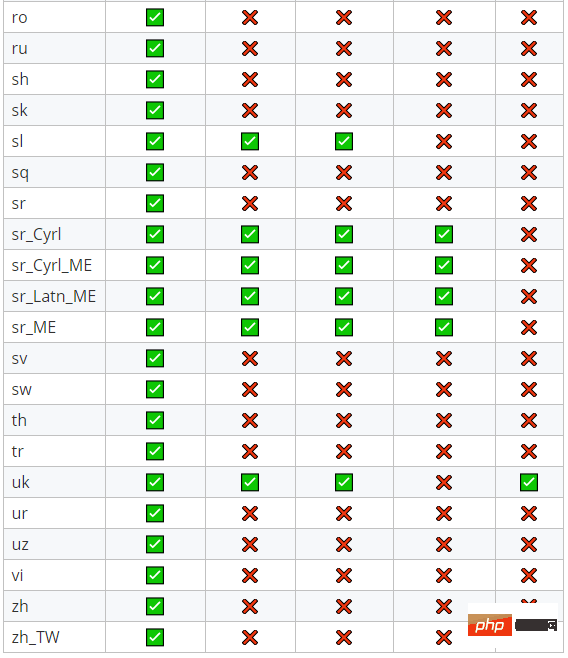
注意,如果您使用Laravel 5.5+,语言环境将根据当前的最后一个App:setLocale execution自动设置。所以扩散人类将是透明的。您可能仍然需要在某些中间件中运行setlocale以使formatlocalizedworking正确。
-
Testing Aids
测试方法允许您在创建“现在”实例时设置要返回的Carbon实例(real或mock)。所提供的实例将在以下条件下具体返回:
对static now()方法的调用,例如 :now()
:now()
当一个空(或空字符串)被传递给构造函数或parse()时,ex.new Carbon(空)
当字符串“now”传递给构造函数或parse()时,ex. new Carbon(‘now’)
给定的实例也将作为diff方法的默认相对时间。
$knownDate = Carbon::create(2001, 5, 21, 12); // create testing date Carbon::setTestNow($knownDate); // set the mock (of course this could be a real mock object) echo Carbon::getTestNow(); // 2001-05-21 12:00:00 echo Carbon::now(); // 2001-05-21 12:00:00 echo new Carbon(); // 2001-05-21 12:00:00 echo Carbon::parse(); // 2001-05-21 12:00:00 echo new Carbon('now'); // 2001-05-21 12:00:00 echo Carbon::parse('now'); // 2001-05-21 12:00:00 echo Carbon::create(2001, 4, 21, 12)->diffForHumans(); // 1 month agovar_dump(Carbon::hasTestNow()); // bool(true) Carbon::setTestNow(); // clear the mock var_dump(Carbon::hasTestNow()); // bool(false)echo Carbon::now(); // 2018-07-05 03:37:12
一个更有意义的完整例子:
class SeasonalProduct { protected $price; public function __construct($price) { $this->price = $price; } public function getPrice() { $multiplier = 1; if (Carbon::now()->month == 12) { $multiplier = 2; } return $this->price * $multiplier;}} $product = new SeasonalProduct(100); Carbon::setTestNow(Carbon::parse('first day of March 2000')); echo $product->getPrice(); //Carbon::setTestNow(Carbon::parse('first day of December 2000')); echo $product->getPrice(); // Carbon::setTestNow(Carbon::parse('first day of May 2000')); echo $product->getPrice(); // Carbon::setTestNow();
根据给定的“now”实例,还可以对相关短语进行嘲笑。
$knownDate = Carbon::create(2001, 5, 21, 12); // create testing date Carbon::setTestNow($knownDate); // set the mock echo new Carbon('tomorrow'); // 2001-05-22 00:00:00 ... notice the time ! echo new Carbon('yesterday'); // 2001-05-20 00:00:00 echo new Carbon('next wednesday'); // 2001-05-23 00:00:00 echo new Carbon('last friday'); // 2001-05-18 00:00:00 echo new Carbon('this thursday'); // 2001-05-24 00:00:00 Carbon::setTestNow(); // always clear it !
被认为是相对修饰语的单词列表如下:
- +
- –
- ago
- first
- next
- last
- this
- today
- tomorrow
- yesterday
请注意,与next()、previous()和modify()方法类似,这些相对修饰符中的一些将把时间设置为00:00。
Carbon: parse($time, $tz)和new Carbon($time, $tz)都可以将时区作为第二个参数。 echo Carbon::parse('2012-9-5 23:26:11.223', 'Europe/Paris')->timezone->getName(); // Europe/Paris
-
Getters
getter方法是通过PHP的__get()方法实现的。这使您能够像访问属性而不是函数调用那样访问值。
$dt = Carbon::parse('2012-10-5 23:26:11.123789'); // 这些getter方法都将返回int类型 var_dump($dt->year); // int(2012)var_dump($dt->month); // int(10) var_dump($dt->day); // int(5) var_dump($dt->hour); // int(23) var_dump($dt->minute); // int(26) var_dump($dt->second); // int(11)var_dump($dt->micro); // int(123789)// dayOfWeek 返回一个数值 0 (sunday) 到 6 (saturday) var_dump($dt->dayOfWeek); // int(5)// dayOfWeekIso 返回一个数值 1 (monday) 到 7 (sunday) var_dump($dt->dayOfWeekIso); // int(5) setlocale(LC_TIME, 'German');var_dump($dt->englishDayOfWeek); // string(6) "Friday"var_dump($dt->shortEnglishDayOfWeek); // string(3) "Fri"var_dump($dt->localeDayOfWeek); // string(7) "Freitag"var_dump($dt->shortLocaleDayOfWeek); // string(2) "Fr"var_dump($dt->englishMonth); // string(7) "October"var_dump($dt->shortEnglishMonth); // string(3) "Oct"var_dump($dt->localeMonth); // string(7) "Oktober"var_dump($dt->shortLocaleMonth); // string(3) "Okt"setlocale(LC_TIME, '');var_dump($dt->dayOfYear); // int(278)var_dump($dt->weekNumberInMonth);// weekNumberInMonth consider weeks from monday to sunday, so the week 1 will// contain 1 day if the month start with a sunday, and up to 7 if it starts with a mondayvar_dump($dt->weekOfMonth); // int(1)// weekOfMonth will returns 1 for the 7 first days of the month, then 2 from the 8th to// the 14th, 3 from the 15th to the 21st, 4 from 22nd to 28th and 5 above var_dump($dt->weekOfYear); // int(40) var_dump($dt->daysInMonth); // int(31) var_dump($dt->timestamp); // int(1349493971) var_dump(Carbon::createFromDate(1975, 5, 21)->age); // int(43) calculated vs now in the same tzvar_dump($dt->quarter); // int(4) // Returns an int of seconds difference from UTC (+/- sign included) var_dump(Carbon::createFromTimestampUTC(0)->offset); // int(0) var_dump(Carbon::createFromTimestamp(0)->offset); // int(-18000) // Returns an int of hours difference from UTC (+/- sign included) var_dump(Carbon::createFromTimestamp(0)->offsetHours); // int(-5)// Indicates if day light savings time is on var_dump(Carbon::createFromDate(2012, 1, 1)->dst); // bool(false) var_dump(Carbon::createFromDate(2012, 9, 1)->dst); // bool(true) // Indicates if the instance is in the same timezone as the local timezone var_dump(Carbon::now()->local); // bool(true)var_dump(Carbon::now('America/Vancouver')->local); // bool(false)// Indicates if the instance is in the UTC timezonevar_dump(Carbon::now()->utc); // bool(false) var_dump(Carbon::now('Europe/London')->utc); // bool(false) var_dump(Carbon::createFromTimestampUTC(0)->utc); // bool(true) // Gets the DateTimeZone instanceecho get_class(Carbon::now()->timezone); // DateTimeZone echo get_class(Carbon::now()->tz); // DateTimeZone// Gets the DateTimeZone instance name, shortcut for ->timezone->getName()echo Carbon::now()->timezoneName; // America/Toronto echo Carbon::now()->tzName; // America/Toronto
-
Setters
下面的setter是通过PHP的__set()方法实现的。值得注意的是,除了显式地设置时区之外,任何设置程序都不会更改实例的时区。具体地说,设置时间戳不会将相应的时区设置为UTC。
$dt = Carbon::now();$dt->year = 1975; $dt->month = 13; //强制 year++ 然后 month = 1 $dt->month = 5; $dt->day = 21; $dt->hour = 22; $dt->minute = 32; $dt->second = 5; $dt->timestamp = 169957925; // 这不会改变时区 // 通过DateTimeZone实例或字符串设置时区 $dt->timezone = new DateTimeZone('Europe/London');$dt->timezone = 'Europe/London';$dt->tz = 'Europe/London';
-
Fluent Setters
对于setter没有可选参数,但是函数定义中有足够的多样性,因此无论如何都不需要它们。值得注意的是,除了显式地设置时区之外,任何设置程序都不会更改实例的时区。具体地说,设置时间戳不会将相应的时区设置为UTC。
$dt = Carbon::now();$dt->year(1975)->month(5)->day(21)->hour(22)->minute(32)->second(5)->toDateTimeString(); $dt->setDate(1975, 5, 21)->setTime(22, 32, 5)->toDateTimeString(); $dt->setDate(1975, 5, 21)->setTimeFromTimeString('22:32:05')->toDateTimeString(); $dt->setDateTime(1975, 5, 21, 22, 32, 5)->toDateTimeString(); $dt->timestamp(169957925)->timezone('Europe/London'); $dt->tz('America/Toronto')->setTimezone('America/Vancouver');
您还可以将日期和时间与其他DateTime/Carbon对象分开设置:
$source1 = new Carbon('2010-05-16 22:40:10'); $dt = new Carbon('2001-01-01 01:01:01'); $dt->setTimeFrom($source1);echo $dt; // 2001-01-01 22:40:10 $source2 = new DateTime('2013-09-01 09:22:56');$dt->setDateFrom($source2);echo $dt; // 2013-09-01 22:40:10
-
IsSet
实现了PHP函数isset()。这是在一些外部系统(例如Twig)在使用属性之前验证属性的存在时完成的。这是使用isset()或empty()方法完成的。在PHP站点:isset()、isset()、empty()上,您可以阅读
 站长资讯网
站长资讯网