本篇文章给大家通过图文方式讲解JS盒子模型的基本属性:clientWidth/Height、offsetWidth/Height、offsetTop/Left、scrollWidth/Height、scrollTop/Left,希望对需要的朋友有所帮助!
写一个JS盒子
<style> .container { width: 300px; height: 300px; border: 3px solid red; margin: 50px; position: relative; } .box { padding: 30px; width: 100px; height: 150px; border: 10px solid lightblue; position: absolute; top: 50px; left: 50px; font-size: 15px; line-height: 100px; text-align: center; overflow: auto; } </style> <body> <div class="container"> <div class="box">盒子</div> </div> </body>
模型: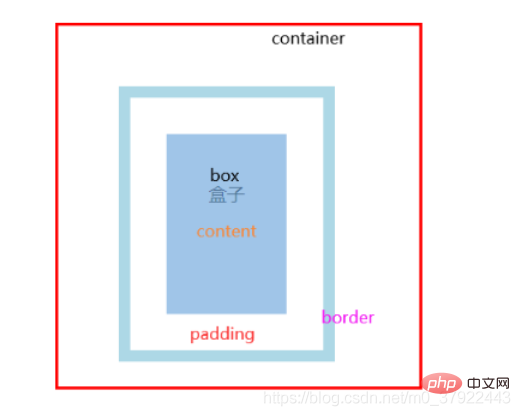
盒子的属性:
client
-
clientWidth / clientHeight :盒子内部的宽高
(1) clientWidth: 内容width + 左右padding
(2) clientHeight: 内容height + 上下padding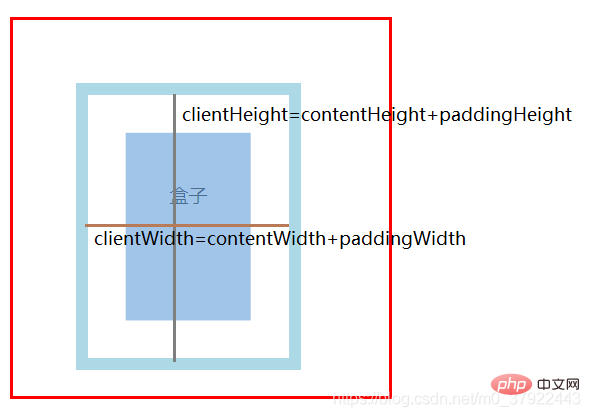
-
clientTop / clientLeft :左边框和上边框的宽度
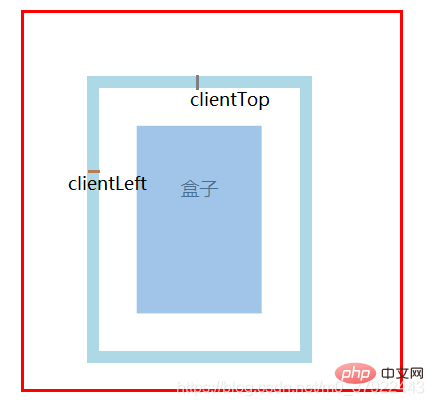
offset
-
offsetWidth / offsetHeight :盒子可见区域的宽高
(1) offsetWidth: clientWidth+ 左右border
(2) offsetHeight: clientHeight+ 上下border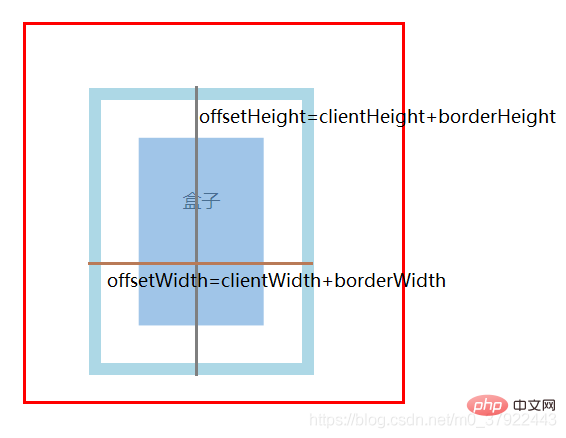
-
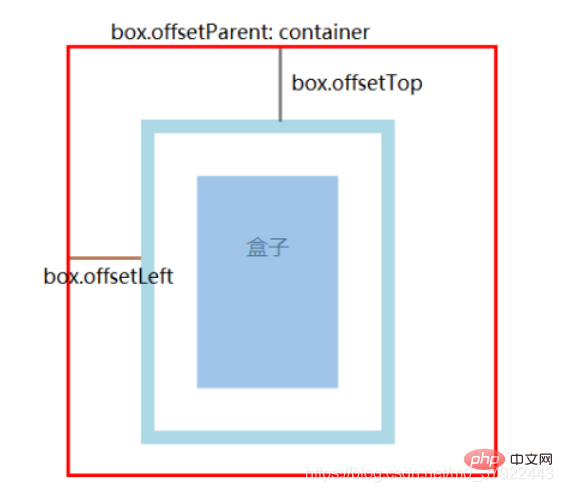
offsetParent:获取它的父参照物(不一定是父元素)
父参照物的查找:
(1) 在同一个平面中,最外层元素是所有后代元素的父参照物;
(2) 而基于position:absolute/relative/fixed会让元素脱离文档流,成为一个新的平面,从而改变元素的父参照物;
(3) body的父参照物为null。 -
offsetTop / offsetLeft:距离其父参照物的上/左偏移(当前元素的外边框到父参照物元素的里边框)
scroll
-
scrollWidth / scrollHeight :可视区内部的真实宽高
(1) 没有内容溢出时: scrollWidth/Height = clientWidth/Height
(2) 有溢出的话不一样,结果约等于盒子真实内容的宽高:上下padding+真实内容的宽高;
(3) 只要出现溢出的情况,overflow的值,也会一定程度地改变scroll的结果。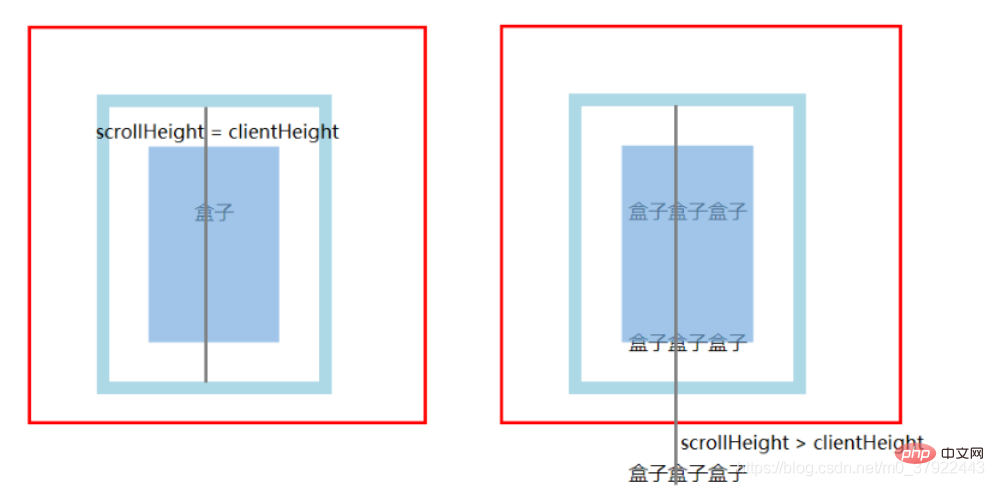
-
scrollTop / scrollLeft:竖向/横向滚动条卷曲的高度/宽度
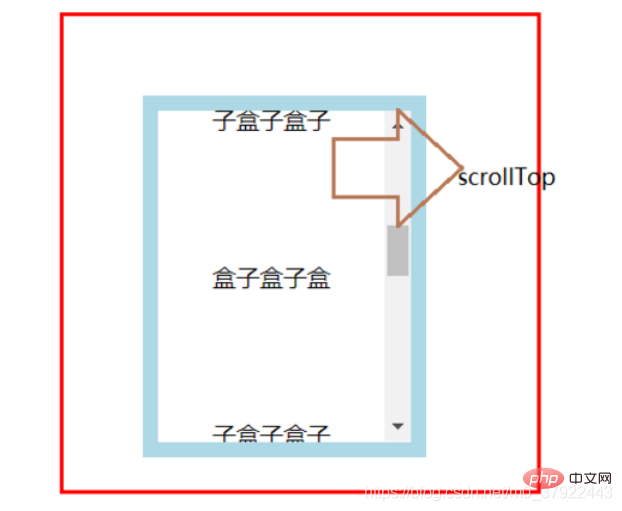
注:上面的属性里,只有scrollLeft和scrollTop可以设置值,其他属性都是只读
 站长资讯网
站长资讯网