本篇文章带大家继续angular的学习,使用angular进行开发时,避免不了需要接触生命周期,下面就来带大家一起聊聊Angular中的生命周期,希望对大家有所帮助!

接触过 react 和 vue 开发的读者应该对生命周期这个概念不陌生。我们在使用 angular 开发的过程中,是避免不了的。
组件从开始建立到销毁的过程中,会经历过一系列的阶段。这就是一个生命周期,这些阶段对应着应用提供的 lifecycle hooks。
那么,在 angular 中,这些 hooks 都有哪些呢?了解它们,对你编写程序应该在哪里编写,很重要。【相关教程推荐:《angular教程》】
angular 中,生命周期执行的顺序如下:
- constructor 【常用,不算钩子函数,但是很重要】 - ngOnChanges【常用】 - ngOnInit【常用】 - ngDoCheck - ngAfterContentInit - ngAfterContentChecked - ngAfterViewInit【常用】 - ngAfterViewChecked - ngOnDestroy【常用】
登录后复制
为了解说和验证,我们用 angular-cli 生成一个 demo 项目。
constructor
在 es6 中的 class 初始化对象的时候,constructor 会立即被调用。
class Person { constructor(name) { console.log('be called') this.name = name; } } let jimmy = new Person('jimmy'); // be called
登录后复制
angular 的组件本身就是导出一个类。当这个组件被 new 起来的时候,会获取 constructor 中的预设的值。
ngOnChanges
当我们有外部参数更改的时候,我们就会执行 ngOnChanges,也就是说组件中有 @Input 所绑定的属性值发生改变的时候调用。
简单说,父组件绑定子组件中的元素,会触发这个钩子函数,可以多次出发。这在下面的 ngOnInit 总会介绍。
ngOnInit
这个方法调用的时候,说明组件已经初始化成功。在第一次 ngOnChanges() 完成之后调用,且只调用一次。
// app.component.ts export class AppComponent implements OnInit, OnChanges { constructor() { console.log('1. constructor') } ngOnChanges() { console.log('2. ngOnChanges') } ngOnInit() { console.log('3. ngOnInit') } }
登录后复制
打印的信息如下:
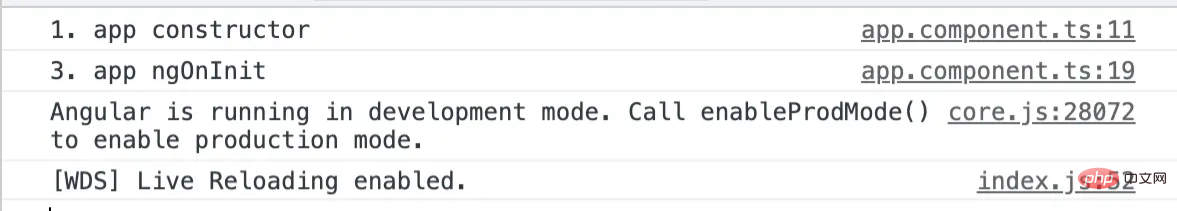
咦?怎么没有打印 ngOnChanges 中的钩子函数信息呢?
上面已经说过了,需要触发条件 @Input 的属性值改变的时候。我们来修改一下:
<!-- app.component.html --> <div> <app-demo></app-demo> </div>
登录后复制
// app.component.ts // AppComponent 类中添加属性 public count:number = 0;
登录后复制
<!-- demo.component.html --> <h3>count: {{ count }}</h3>
登录后复制
// demo.component.ts export class DemoComponent implements OnInit, OnChanges { @Input() public count: number; constructor() { console.log('1. demo constructor') } ngOnChanges() { console.log('2. demo ngOnChanges') } ngOnInit() { console.log('3. demo ngOnInit') } }
登录后复制
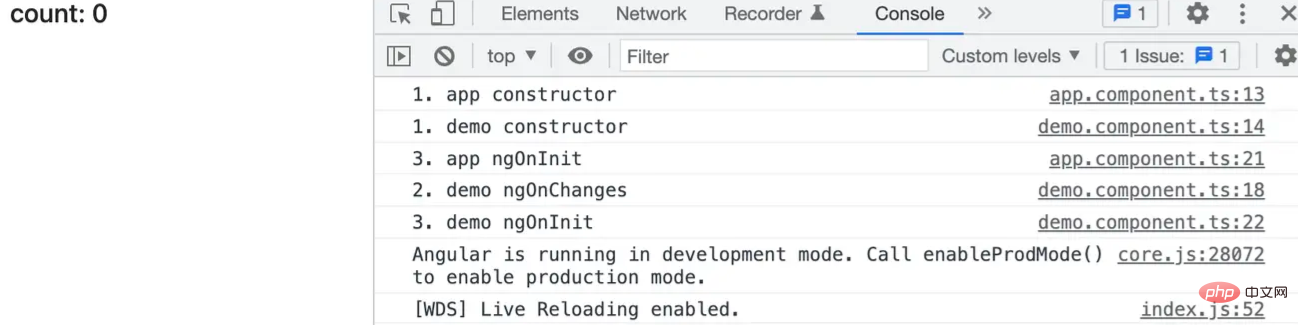
当通过 @Input 将值传递给子组件 demo 的时候,就会触发 demo 组件中的 ngOnChanges。
当 @Input 传递的属性发生改变的时候,可以多次触发 demo 组件中的 ngOnChanges 钩子函数。
<!-- app.component.html --> <div> <app-demo [count]="count"></app-demo> <button (click)="parentDemo()">parent button</button> </div>
登录后复制
// app.component.ts parentDemo() { this.count++; }
登录后复制
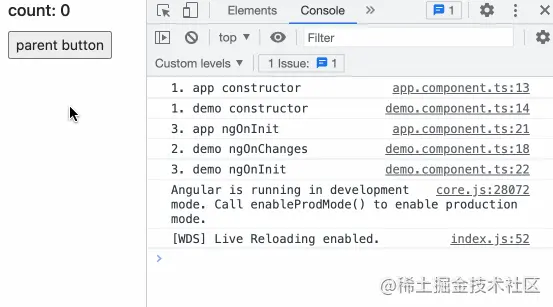
ngDoCheck
当发生变化检测的时候,触发该钩子函数。
这个钩子函数,紧跟在每次执行变更检测时候 ngOnChanges 和首次执行执行变更检测时 ngOnInit 后面调用。
// demo.component.ts ngDoCheck() { console.log('4. demo ngDoCheck') }
登录后复制
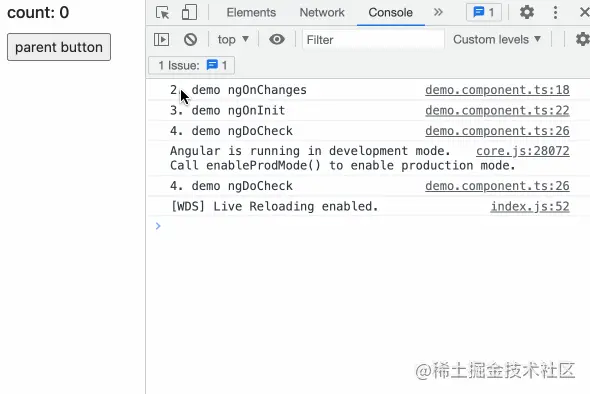
这个钩子函数调用得比较频繁,使用成本比较高,谨慎使用。
一般使用 ngOnChanges 来检测变动,而不是 ngDoCheck
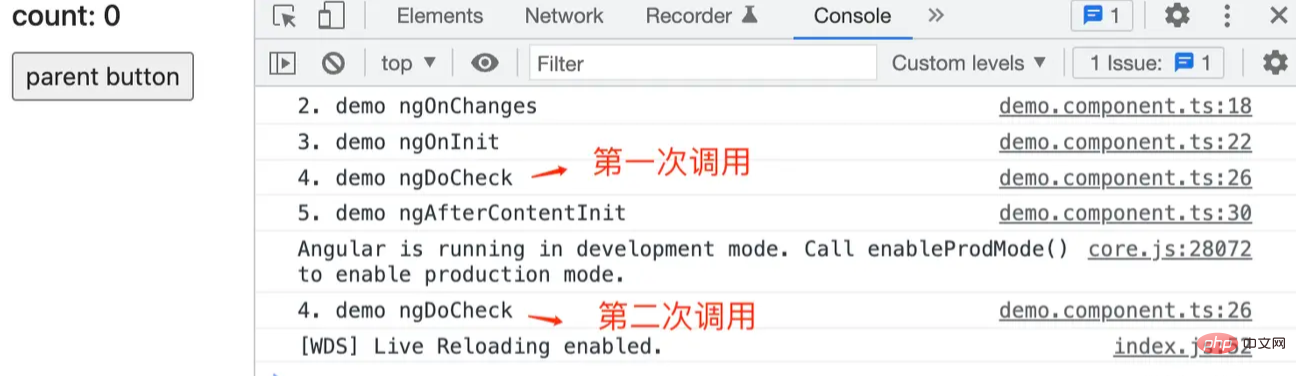
ngAfterContentInit
当把外部的内容投影到内部组件,第一次调用 ngDoCheck 之后调用 ngAfterContentInit,而且只调用一次。
// demo.component.ts ngAfterContentInit() { console.log('5. demo ngAfterContentInit'); }
登录后复制
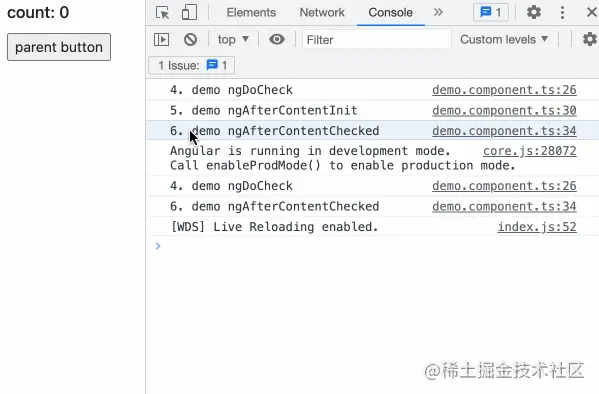
ngAfterContentChecked
ngAfterContentChecked 钩子函数在每次 ngDoCheck 之后调用.
// demo.component.ts ngAfterContentChecked() { console.log('5. demo ngAfterContentChecked'); }
登录后复制
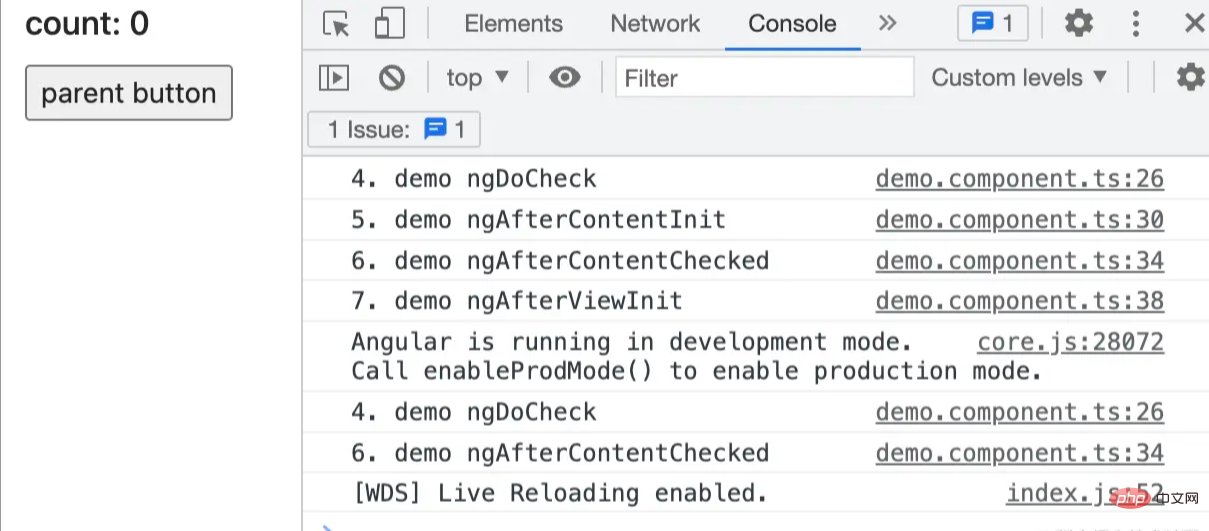
ngAfterViewInit
视图初始化完成调用此钩子函数。在第一次 ngAfterContentChecked 之后调用,只调用一次。
这个时候,获取页面的 DOM 节点比较合理
// demo.compoent.ts ngAfterViewInit() { console.log('7. demo ngAfterViewInit'); }
登录后复制
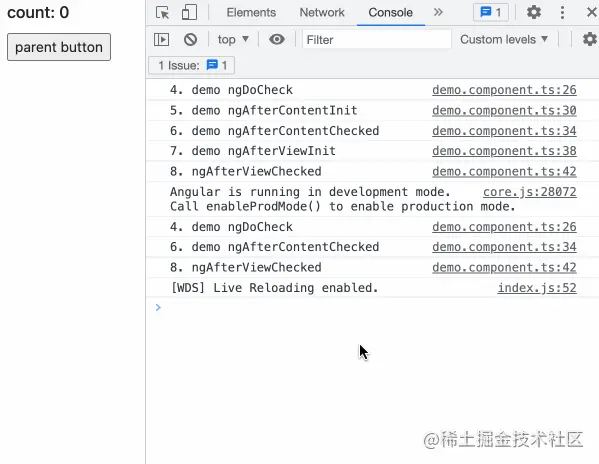
ngAfterViewChecked
视图检测完成调用。在 ngAfterViewinit 后调用,和在每次 ngAfterContentChecked 之后调用,也就是在每次 ngDoCheck 之后调用。
// demo.component.ts ngAfterViewChecked() { console.log('8. ngAfterViewChecked') }
登录后复制
ngOnDestroy
组件被销毁时候进行的操作。
在这个钩子函数中,我们可以取消订阅,取消定时操作等等。
<!-- app.component.html --> <app-demo [count]="count" *ngIf="showDemoComponent"></app-demo> <button (click)="hideDemo()">hide demo component</button>
登录后复制
// app.component.ts public showDemoComponent: boolean = true; hideDemo() { this.showDemoComponent = false }
登录后复制
// demo.component.ts ngOnDestroy() { console.log('9. demo ngOnDestroy') }
登录后复制
PS: 不知道读者有没有发现,调用一次的钩子函数都比较常用~
 站长资讯网
站长资讯网