
PHP是如何做垃圾回收的?
包含 php 5 与 php7 的变量实现和垃圾回收的对比
变量的实现
PHP 的变量是弱类型的,可以表示整数、浮点数、字符串等类型。PHP 的变量是使用结构体 zval 表示的
PHP 5.* zval 和 zend_value 结构
struct _zval_struct { // 结构体 zvalue_value value; zend_uint refcount__gc; zend_uchar type; zend_uchar is_ref__gc; } typedef union _zvalue_value { // 联合体 long lval; double dval; struct { char *val; int len; } str; // 字符串 HashTable *ht; // 数组 zend_object_value obj; // 对象 zend_ast *ast; } zvalue_value;
PHP 7.0 zval 和 zend_value 结构
struct _zval_struct { union { zend_long lval; /* long value */ double dval; /* double value */ zend_refcounted *counted; zend_string *str; zend_array *arr; zend_object *obj; zend_resource *res; zend_reference *ref; zend_ast_ref *ast; zval *zv; void *ptr; zend_class_entry *ce; zend_function *func; struct { uint32_t w1; uint32_t w2; } ww; } value; union { struct { ZEND_ENDIAN_LOHI_4( zend_uchar type, /* active type */ zend_uchar type_flags, zend_uchar const_flags, zend_uchar reserved) /* call info for EX(This) */ } v; uint32_t type_info; } u1; union { uint32_t var_flags; uint32_t next; /* hash collision chain */ uint32_t cache_slot; /* literal cache slot */ uint32_t lineno; /* line number (for ast nodes) */ uint32_t num_args; /* arguments number for EX(This) */ uint32_t fe_pos; /* foreach position */ uint32_t fe_iter_idx; /* foreach iterator index */ } u2; };
PHP5 与 PHP7 引用计数的对比
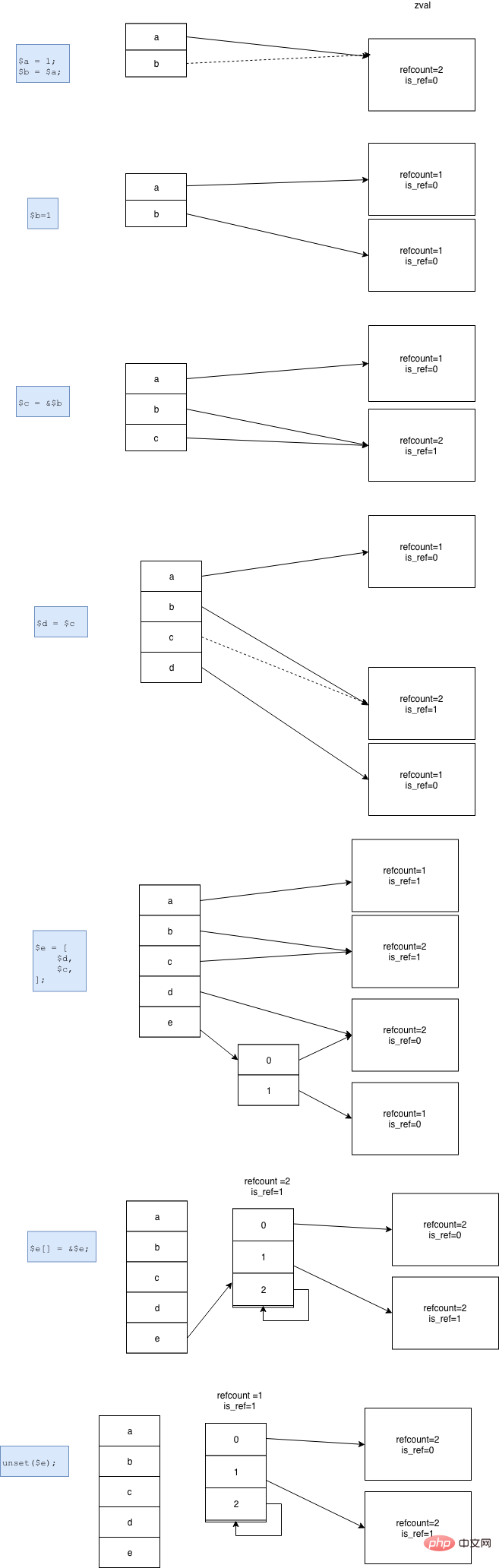
php 5.* 变量赋值等操作引用计数如图所示,在倒数第二步,会形成一个循环引用,并且在 unset 操作之后,会产生垃圾。
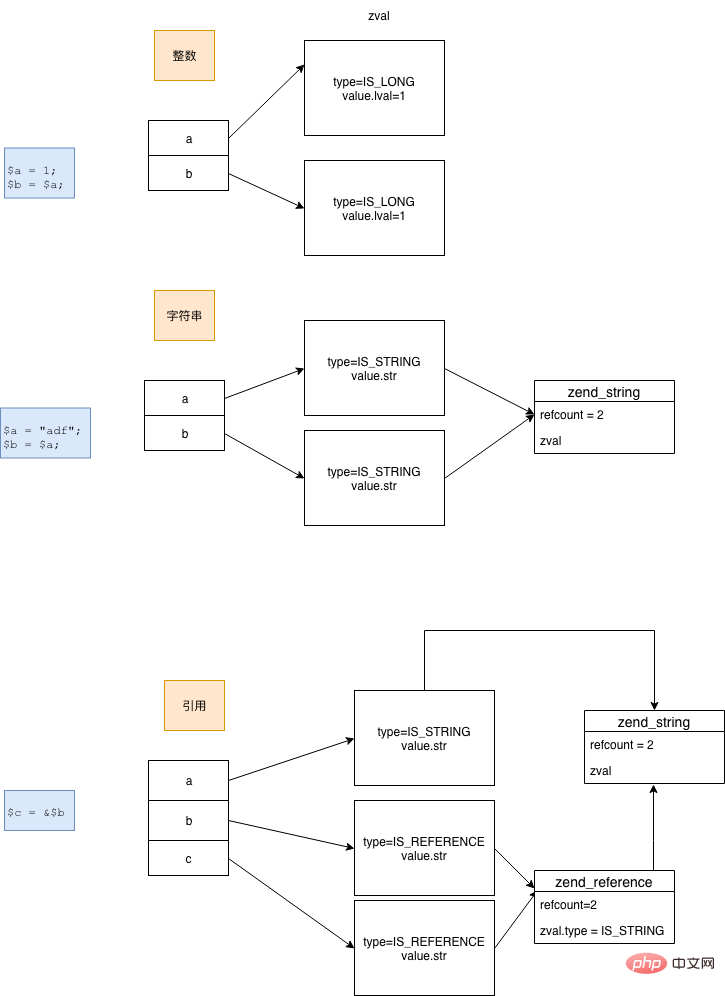
PHP 7 的计数放到了具体的 value 中,zval 不存在写时复制(写时分离)。
并且 PHP 7 的有一个专门的 zend_reference 用来表示引用。
有了以上关于 PHP 变量存储的知识,我们可以理解一下 PHP 是如何做垃圾回收的了。
什么是垃圾
首先,我们需要定义什么是垃圾。
1. refcount 增加的不是
2. refcount 等于0的不是,这个会被直接清除
3. refcount 减少,并且不等于0的才是垃圾
垃圾收集
1. php7 要求数据类型是数组和对象,并且 type_flag 是 IS_TYPE_COLLECTABLE
2. 没有在缓冲区中存在过
3. 没有被标记过
4. 标记为紫色,并且放到缓冲区中
回收算法
论文:https://researcher.watson.ibm.com/researcher/files/us-bacon/Bacon01Concurrent.pdf
PHP 5.3 版本以及之后的版本
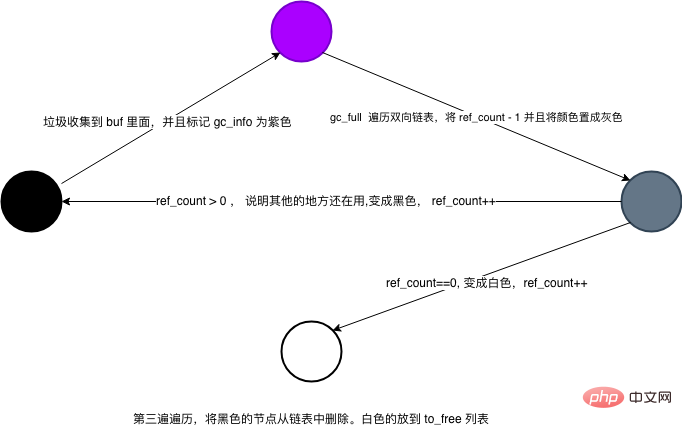
1. 将垃圾放到一个 root 池中
2. 当满 10000 个节点的时候进行垃圾回收
3. 遍历双向链表中的节点 refcount-1
4. 遍历双向链表将 refcount=0 的节点删除,到free队列中
5. 对 refcount!=0 的 refcount+1
 站长资讯网
站长资讯网